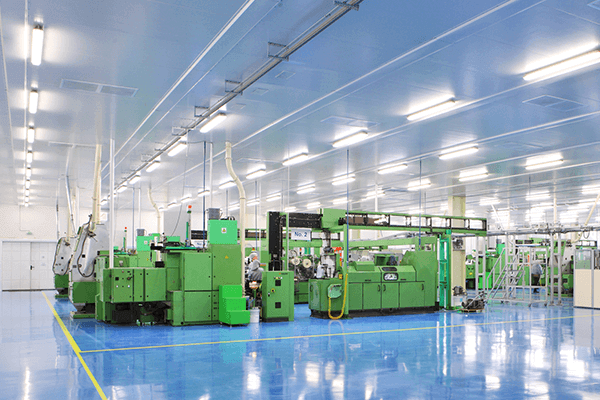
ISO 8 cleanrooms are controlled environments designed to maintain moderate levels of airborne particles and contamination. Unlike higher-class cleanrooms such as ISO 5 or ISO 6, ISO 8 cleanrooms allow for a greater concentration of particles while still providing a controlled and hygienic environment. These cleanrooms are widely used across industries where precision, contamination control, and compliance with regulatory standards are important, but the processes are less sensitive to ultra-low particle counts.
Industries that rely on ISO 8 cleanrooms include pharmaceuticals, electronics, food and beverage production, medical devices, and cosmetics. These facilities require environments that limit dust, particulate matter, and microbial contamination to ensure product quality and safety. Organizations investing in an ISO 8 Cleanroom do so to meet regulatory requirements, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of contamination in processes that, while critical, do not require the extremely strict particle limits of higher-class cleanrooms.
Pharmaceutical Industry Applications
In the pharmaceutical sector, ISO 8 cleanrooms are often used for non-sterile manufacturing processes, such as tablet formulation, packaging, and secondary production. While ISO 5 or ISO 7 cleanrooms are necessary for aseptic or sterile drug production, ISO 8 environments provide sufficient contamination control for less sensitive operations. The controlled environment helps minimize dust, particulate contamination, and microbial growth, protecting product quality and complying with regulatory standards.
ISO 8 cleanrooms in pharmaceutical manufacturing often incorporate features such as HEPA-filtered air, controlled airflow patterns, and temperature and humidity regulation. These measures ensure that the environment supports safe and consistent production while reducing the risk of contamination that could affect product efficacy or shelf life.
Electronics and Semiconductor Applications
Electronics and semiconductor manufacturing also benefit from ISO 8 cleanroom environments. Processes such as assembly of printed circuit boards, component testing, and packaging require controlled conditions to prevent dust and particulate contamination, which can affect product performance. ISO 8 cleanrooms provide a balance between cleanliness and operational flexibility, allowing these processes to be carried out efficiently without the extreme restrictions of higher-class cleanrooms.
Air filtration, regular monitoring, and proper workflow design in ISO 8 cleanrooms help prevent contamination from human activity, equipment, and materials. This ensures that sensitive electronic components maintain reliability and meet quality standards.
Food and Beverage Industry Applications
ISO 8 cleanrooms are increasingly used in the food and beverage industry, particularly in high-value or specialty product manufacturing. These cleanrooms provide controlled conditions for packaging, processing, and quality control to minimize microbial contamination, dust, and other particulate matter. For example, cleanroom environments may be used in the production of dietary supplements, powdered products, or ready-to-eat meals, where contamination could compromise safety and regulatory compliance.
Temperature and humidity control, combined with proper cleaning and sanitation protocols, ensures that ISO 8 cleanrooms in the food industry maintain product quality and extend shelf life. These cleanrooms also help facilities meet industry-specific hygiene regulations and consumer safety standards.
Medical Devices and Cosmetics
The production of medical devices and cosmetic products also relies on ISO 8 cleanrooms for contamination control. In medical device manufacturing, processes such as assembly, inspection, and packaging require environments that limit particulate and microbial contamination. ISO 8 cleanrooms provide sufficient control to ensure product safety and compliance with regulatory guidelines without the operational complexity of higher-class cleanrooms.
In the cosmetics industry, ISO 8 cleanrooms are used for filling, packaging, and quality control of creams, lotions, and other personal care products. Contamination control in these environments ensures product consistency, safety, and compliance with consumer protection regulations.
Operational Considerations
Maintaining an ISO 8 cleanroom requires attention to airflow, filtration, personnel protocols, and environmental monitoring. While these cleanrooms are less stringent than ISO 5 or ISO 6 environments, they still require HEPA filtration, controlled entry points, and proper gowning procedures to minimize contamination. Regular cleaning, monitoring, and validation of particle levels and environmental conditions ensure that the cleanroom maintains its designated ISO classification.
Personnel training is a key component of ISO 8 cleanroom operations. Employees must follow proper hygiene, gowning, and material handling protocols to prevent introducing particles or microorganisms into the environment. Equipment and materials must also be compatible with cleanroom standards to minimize contamination risks.
Advantages Across Industries
The use of ISO 8 cleanrooms provides industries with a cost-effective and practical solution for contamination control. They offer sufficient cleanliness for many manufacturing and assembly processes without the high operational costs and restrictions associated with higher-class cleanrooms. ISO 8 cleanrooms also allow greater flexibility in workflow and equipment placement, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
In conclusion, ISO 8 cleanrooms play a vital role across multiple industries by providing controlled environments that balance contamination control, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. From pharmaceuticals and electronics to food production and cosmetics, these cleanrooms ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and safety while supporting reliable and efficient manufacturing operations. Their versatility makes ISO 8 cleanrooms an essential tool for organizations seeking controlled environments without the stringent requirements of higher-class cleanrooms.